MHC (HSA 1/6/9/19) Paralogon Information
The MHC of gnathostomata is defined as a big genetic region of ∼4 megabases (Mb) encrypt more than 100 genes, majority of which are concerned with immunity (Horton et al., 2004). Major MHC paralogon maps to human chromosomal regions 1, 6, 9 and 19, but mini MHC paralogons are also identified and reported on some other portions of human chromosomes like Hsa5, Hsa12 and Hsa15. These mini paralogons are assumed to be formulated from disintegrating and sub-sequent translocation of the major MHC paralogon (Flajnik and Kasahara, 2001; Horton et al., 2004). Major MHC paralogon is classified into three main classes: Class I , class II and class III. Class I and II encode the polymorphic Ag-presenting molecules and genes involved in Ag processing pathways (Henry et al., 1997). The gene-dense class III region encodes a number of complement components and additional genes implicated in inflammation (Trowsdale and Knight, 2013). Exploration about the foundation of MHC paralogon revealed that invertebrates such as amphioxus and C.Intestinalis have a solo MHC-like region that is nominated as a precursor of the four MHC paralogons in modern jawed vertebrates (Abi-Rached et al., 2002; Kasahara et al., 2004). In simpler terms, the crucial masterpiece of the MHC-linked region was assembled earlier than the evolution of vertebrates, over 525 million years back and then grew up by gene/genome duplication events (Smith et al., 2001). Therefore, MHC paralogon has appeared as a model to scrutinize the timing and nature of duplications projected by 2R hypothesis.
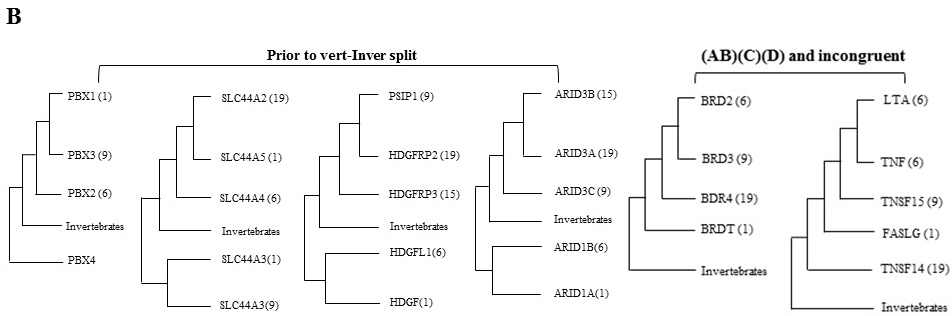
Figure 1: Graphical representation of quadruplicated gene families depicts paralogy regions spanning on MHC (HSA 1/6/9/19). (A) Paralogus genes of each family are coded with same color. These genes are also syntenicly mapped on respective chromosomes. (B) Schematic NJ tree topologies of multigene families constituting on human MHC (HSA 1/6/9/19) paralogon (see panel A). Two different types of topologies are obtained and delineated by bracket symbols. Diversification of PBX, SLC44A, HDGF and ARID families involved duplication occurring prior to vertebrate-invertebrate split (left panel). The incongruent type topology of BRDT and TNF families presents vertebrate specific duplication history. Phylogenomic analysis of multigene families depicts different time points and different patterns of duplication spread across history of animal lineage.
Useful references: